What is S thermocouple?
Thermocouple S, also known as type S thermocouple, type S thermocouple or S thermocouple sensor – English name is Thermocouple Type S, is a type of temperature sensor used to measure high temperatures from 0° C up to 1600°C in industrial applications. The probe part of the thermocouple is usually ceramic-coated, ensuring that the thermocouple can operate in the high temperature range. This type of thermocouple is often used in high-temperature applications such as furnaces, furnaces, boilers, steelmaking, thermochemical reactions, etc.

Structure and operating principle of S-type thermocouple
1. Structure of S thermocouple
The S thermocouple sensor is made up of 90% PT and 10% Rh-Pt, also known as ceramic. On the outside, they have a similar shape to other types of thermocouples. Platinum, also known as platinum, has the chemical symbol Pt – this is one of the rarest elements in the Earth’s crust with an average distribution density of only 0.005mg/kg. It is grey-white, shiny, dense and malleable in its pure form. This type also has a closer name that is often used in jewelry called white gold. Platinum does not oxidize in any thermal environment, is insoluble in acids (inert), is electrically conductive and is less susceptible to corrosion. It is only soluble in some halogen cyanide solutions or aqua regia. Platinum is widely used in industries such as: automobile industry (accounting for more than 50% of annual output), jewelry, medicine (manufacturing medical equipment, machinery, cancer chemotherapy drugs) … This versatility makes it an extremely rare metal. Rhodium has the chemical symbol Rh, is a silver-white, hard and durable transition metal. Thanks to its special chemical properties, Rhodium does not corrode and oxidize, and is less susceptible to fading and scratches. The only substance that can corrode Rhodium is sulfuric acid. Thanks to its extremely high light reflection properties, this is a rare feature of metals, so it is often used in the jewelry industry along with silver and other materials to create beautiful jewelry. and valuable thanks to plating technology. There are a few different types of thermocouples, but basically, they all include the following main parts:
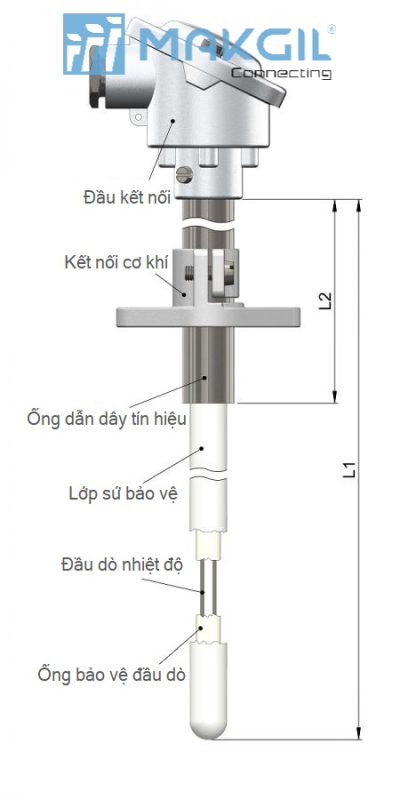
Connection head
Also known as the protective head or onion head, usually made from aluminum or stainless steel, it is a mechanical part that protects the connection bridge and internal signal wires. This signal wire is often connected to the control PLC or display screen, warning device, or alarm. Normally, type S thermocouples will have an additional 4-20mA output signal option, this type will have an integrated temperature converter inside this protective head.
Signal conduit
It is a metal structure that connects the connection head to the ceramic measuring rod, inside are two capillary tubes that protect the signal wire transmitted from the sensor head. This is a highly heat-resistant position, so it is usually made from SUS316 stainless steel, Inconel or aluminum that can withstand high temperatures and help dissipate heat in the measurement area.
Process connection
Is the connection part that helps fix the S thermocouple to the system or equipment to be measured. According to the standard, these type S thermocouples do not have a threaded connection, but the sensor part will drop directly into the measurement position. However, there will usually be flange or threaded connection accessory options included, helping users fix the thermocouple to the device or system.
Protective ceramic layer (Inner tube)
The probe part of the sensor is covered by many different ceramic layers, in which the outermost protective ceramic layer has a thickness suitable for the temperature to be measured, and must also have high hardness, impact resistance and resistance. heat transfer to the inside.
Insullation rod
Located between the outer protective ceramic layer and the temperature probe is another mixed ceramic layer, which helps fix and protect the inner temperature probe at the same time, avoiding external influences. There must be a certain distance between these two ceramic layers, ensuring the ability to transfer heat without being affected by expansion in the high temperature environment of the sensor.
Temperature probe (measuring sensor)
Is the part located in the innermost part of the measuring probe, considered the heart of the thermocouple, directly sensing the temperature value, through the signal wire to notify the measured temperature value. Temperature probes usually have two sizes, corresponding to two different temperature ranges:
- Diameter 0.35mm: corresponding to temperature range 1350°C
- Diameter 0.5mm: corresponding to 1600°C temperature range
2. Operating principle of S thermocouple
Thermocouple thermocouples all have the same operating principle, only the constituent materials differ. Thermocouples are made up of two different metal wires welded together, one end is called the hot end (or measuring end), the other end is called the cold end (or standard end). When there is a temperature difference between the hot end and the cold end, an electromotive force V will arise at the cold end. One problem is to stabilize and measure the temperature at the cold end, this depends greatly on the material. Defined another way, a thermocouple is a closed-circuit thermoelectric sensing device consisting of two dissimilar metal wires connected at both ends. An electric current is generated when the temperature at one end is different from the temperature at the other end. This phenomenon is known as the Seebeck effect, which is the basis for measuring temperature with thermocouples. Thermocouples operate on the principle of “thermoelectric effect”. This effect occurs when two dissimilar metals are joined together at one end, generating a very small electric current measured in millivolts (mV). When the temperature at this junction changes, the internal current changes > Based on this electrical signal, the temperature value will be read.

Distinguish between S and Pt100 thermocouple sensors
Type S thermocouples and Pt100 temperature sensors both have the same purpose of measuring and controlling the temperature of equipment and systems and both have relatively similar external shapes. However, because they are different in structure and operating principle, they have some of the following differences:
1. About structure
Pt100 is composed of metal wire made from: Copper, Nickel, Platinum,… wrapped in the shape of the big head. When the temperature changes, the resistance between the two ends of the metal wire will change, and depending on the metal material, there will be linearity within a certain temperature range. Type S thermocouples are composed of two different metal wires welded together. One end is called the hot end (or measuring end), the other two ends are called cold ends (or standard ends). When there is a temperature difference between the hot end and the cold end, an electromotive force V will arise at the cold end. When the temperature at this connection point changes, the internal current will change, then based on this electrical signal, the temperature value will be read.
2. About function
- Pt100 is used to measure temperature in the range of -200°C…850°C.
- Thermocouple S is used to measure temperature in the range 0°C…1600°C.
Advantages and disadvantages of type S thermocouples
Advantage
- Excellent temperature measurement ability, up to 1600°C.
- Can be used in most applications requiring direct temperature measurement.
- Diverse designs in length, wire type, connection type, etc. to suit most customer requirements.
Defect
- Due to the characteristics of being used to measure high temperatures, being made up of two rare metals, the S thermocouple has a quite high price.
- Because the outer protective layer is made of ceramic, it can easily break when exposed to strong impacts.
- The accuracy level is not as high as the Pt100 temperature sensor.
Criteria for choosing to buy S thermocouples
When choosing a type S thermocouple, users should pay attention to some basic criteria, ensuring the choice of a thermocouple that best suits their application and purpose of use. Below are some basic criteria to help users more conveniently choose:
- Measuring range: Because the S thermocouple is used to measure quite high working temperatures – up to 1600°C, when choosing, users should accurately determine the temperature range to be measured, helping to ensure the working conditions of the device. equipment and cost optimization.
- Connector material: Normally, the connector part often has material options such as aluminum, stainless steel, etc. This greatly affects the product price, so you need to consider when choosing.
- Protection tube diameter: Users need to check and choose the appropriate protection tube diameter size to avoid difficulties during installation.
- Temperature probe size: As mentioned above in the structure, the S thermocouple has a temperature probe with 02 size options, corresponding to 02 temperature ranges to be measured. Người dùng nên lưu ý để lựa chọn cho phù hợp, cụ thể:
- Diameter 0.35mm: corresponding to temperature range 1350°C
- Diameter 0.5mm: corresponding to 1600°C temperature range
- Mechanical connection: Users need to check the connection of existing systems and equipment to choose the appropriate thermocouple connection to ensure the installation process. The two most common connections are threaded connections and flanged connections.
- Accuracy: Thermocouples often have different levels of accuracy and they determine the error of the product and the selling price of the thermocouple, so users need to understand clearly to choose.
- Working medium: To determine if the included thermowell protection tube is needed? For environments with high pressure or corrosive and oxidizing media, it is often necessary to use a thermowell tube to protect the probe.
- Measuring probe length: Users need to choose the appropriate length of the sensor to avoid cases where the length is too long, leading to difficulty in installation, or too short, leading to inaccurate thermocouple measurements.
- Output signal: Normally, type S thermocouple sensors have two types of output signals: millivoltage or analog 4-20mA. Depending on the purpose of use, users should consider choosing to suit their usage requirements.
Commonly used temperature measurement units
Below are some popular temperature measurement units in the industrial sector in the Vietnamese market:
- Convert °F to °C: °C = (°F – 32) / 1.8
- Convert degrees Celsius to degrees Fahrenheit: °F = °C × 1.8 + 32
- Convert from degrees K to degrees Celsius: °C = K – 273.15
- Convert from °C to K: K = °C + 273.15
Makgil specializes in providing genuine S thermocouples, made in Europe
Makgil Vietnam is one of the most experienced units in the field of supply and installation of pressure and temperature measuring equipment, including thermocouples. With many years of experience in the industry, Makgil is currently an authorized distributor of Thermo-electra from Netherland – a brand since 1962 with a full range of products, superior quality and technology. With a team of experienced staff, we can easily advise customers on choosing the type of watch that suits their requirements and purpose, with the most optimal and reasonable cost. In particular, with a very large amount of goods in stock with a full range of types, measuring ranges, materials, sizes, and prices, Makgil Vietnam always commits to being the best in the market, with a warranty period of up to 18 months, ensuring Guaranteed so customers can choose with confidence. Customers please note that we do not provide goods originating from China, with Chinese brands, affecting our reputation and the safety of users’ systems. Makgil Vietnam is pleased to serve all customer requests according to the details below: MAKGIL VIETNAM COMPANY LIMITED
- Head office: 18/21 Nguyen Van Dung, Ward 06, Go Vap District, City. Ho Chi Minh
- Hanoi Branch: No. 130 D4 Dai Kim New Urban Area, Dai Kim, Hoang Mai, Hanoi
- Phone: 02866-572-704
- Fax: 02822-026-775
- Website: https://makgil.com Email: info@makgil.com
- Zalo: 0902 949 401 – 0902 988 005 – 0932 798 882


